The following essay is reprinted with permission from ![]() The Conversation, an online publication covering the latest research.
The Conversation, an online publication covering the latest research.
Picture two homes on the same street: one constructed in the 1950s and the other in the 1990s. There are no trees or other shade. The air conditioning units are identical, recently replaced, and operating perfectly. Identical thermostats are set at 82 degrees Fahrenheit (27.8 Celsius).
When it’s 110 F (43.3 C) outside, the 1950s house will likely feel at least 10 F (5.6 C) warmer inside, even with the same air temperature.
Why?
The answer has to do with radiant heat. Radiant heat is what keeps you toasty warm at a campfire on a cold winter night. The fire doesn’t warm the air much; rather, like the Sun, most of the fire’s heat moves through invisible waves directly from the campfire to your body.
In the radiant heat of the Arizona sun, the surface temperature of the uninsulated post-and-beam ceilings in my house, one of 41,000 built in Tucson during the post-World War II era, can reach over 100 F (37.8 C). The single-glazed steel windows register 122 F (50 C), and the uninsulated concrete block walls aren’t much cooler.
Inside my house on triple-digit days, it can feel like I’m standing near a campfire, even with the air conditioner roaring to maintain 75 F (23.9 C). And when the system breaks – as it did during the long-running 2023 heat wave, when Phoenix hit 110 F (43.3 C) every day for weeks – temperatures rise dangerously fast. Without the AC, the hot surfaces plus the swirl of air from the ceiling fan makes the house feel like an air fryer.
Air temperature: An incomplete indicator of comfort
While people are used to thinking about how clothing, air movement, temperature and humidity affect comfort, two lesser-known measures help explain how they experience comfort indoors:
-
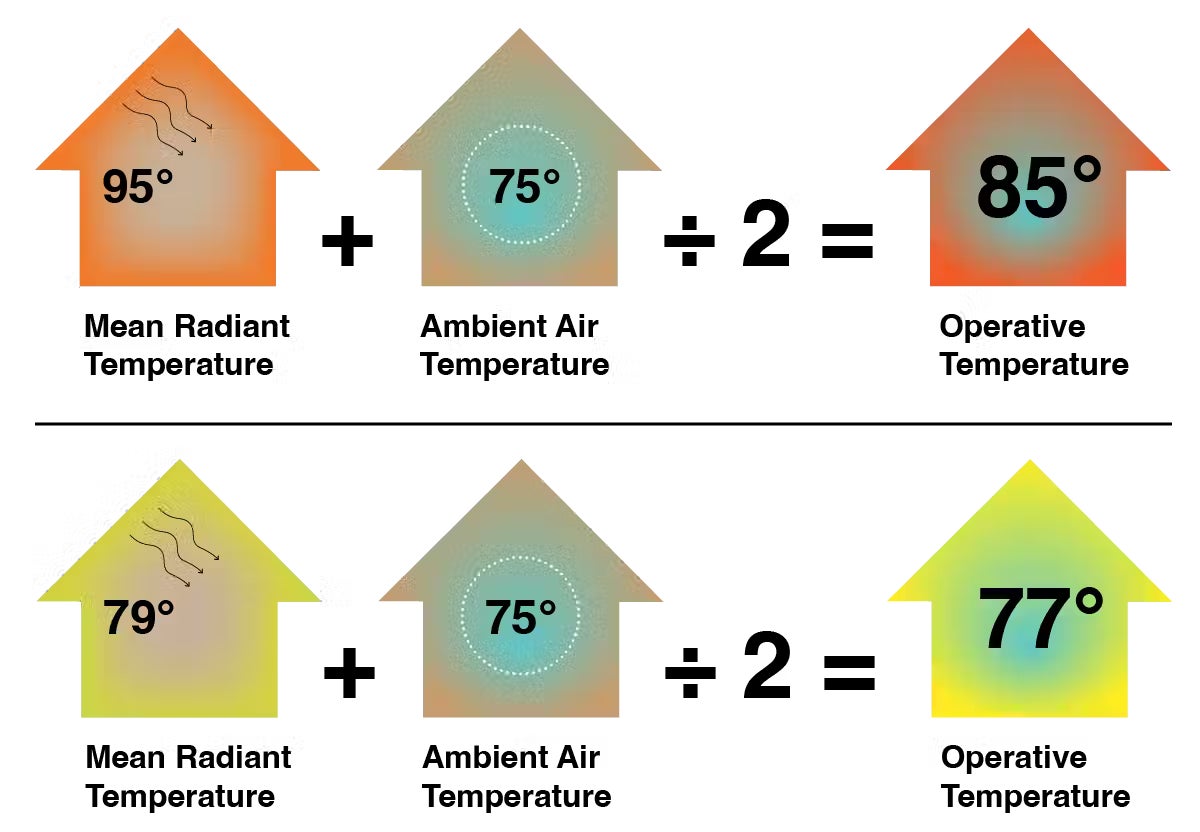
Mean radiant temperature. This is the average temperature of all the surfaces that surround us: ceiling, windows, walls, floor. For radiant heat to move between an object and the human body, it needs an uninterrupted line of sight, so ceilings and unobstructed windows have an outsized influence on the radiant temperature experienced in a specific place in a house.
-
Operative temperature. This can be approximated by averaging the mean radiant temperature and the average air temperature in a room. Other calculations of operative temperature take into account effects of air movement, humidity and additional variables. Roughly half of how you experience comfort is determined by the radiant environment.
Unfortunately, as the building scientist Robert Bean (no relation) says, “an entire industry of manufacturers, suppliers, builders and tradespeople incorrectly equate thermal comfort with air temperatures.” The result is that most people are completely oblivious to what actually makes a space feel comfortable — or uncomfortably hot.
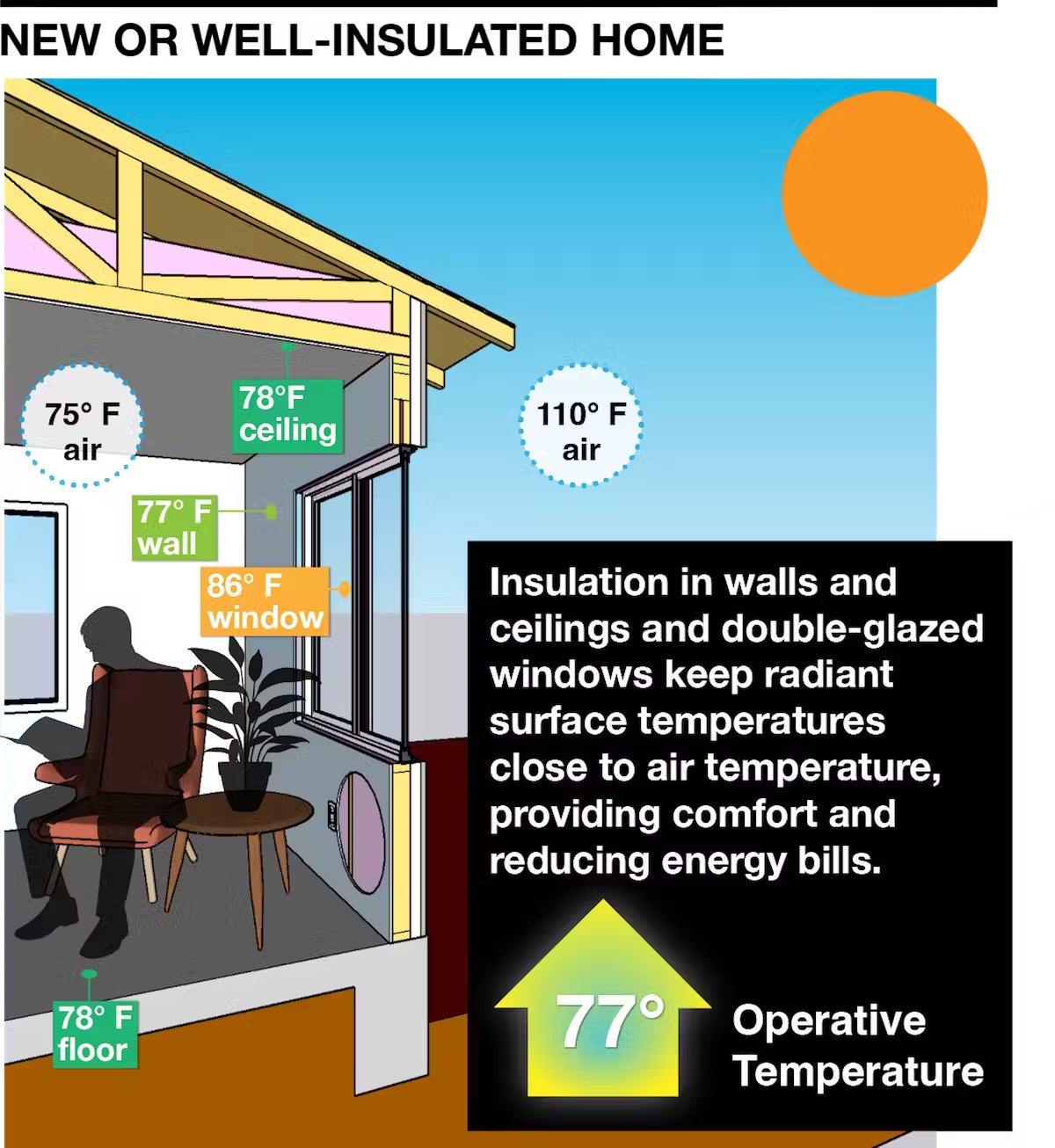
On a hot, sunny day, good insulation and double-pane windows slow heat transfer enough for air conditioning to keep the mean radiant temperature inside the building within a few degrees of the air temperature.
However, in an under-insulated building, such as my house, or in some older public housing projects in Phoenix, the high mean radiant temperature can push the operative temperature over 90 F (32.2 C) – even with the thermostat set to 75 F (23.9 C). When the surface temperature exceeds the temperature of our skin, heat will begin to radiate from the hot surface into the body, making heat stroke more likely.
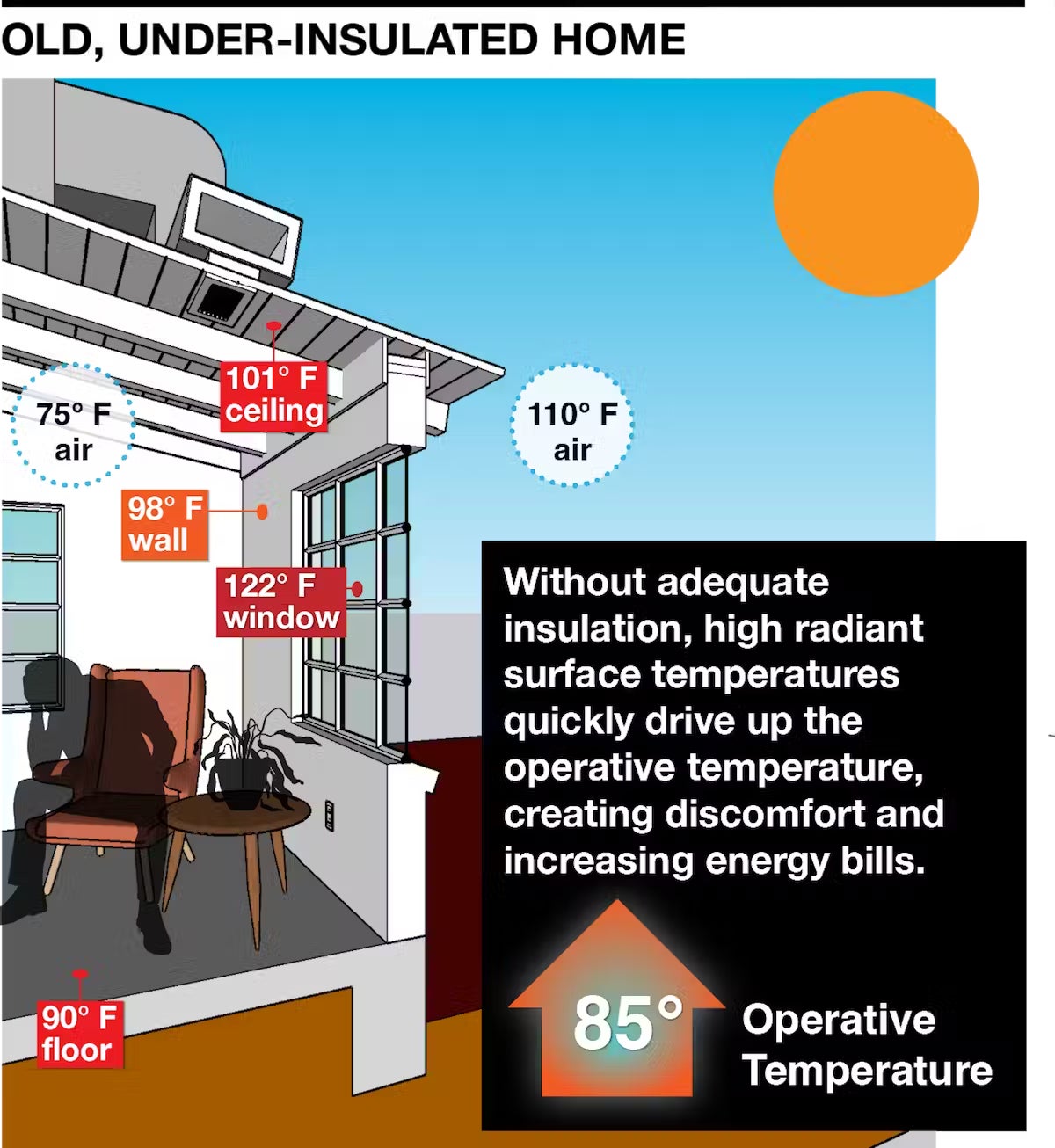
While the exact threshold where overheating becomes dangerous is debated, most people would agree that 90 F (32.2 C) is far too warm for comfort.
Hot surfaces are why smaller buildings, such as mobile homes, tiny homes, shipping containers and garages turned into apartments, often feel uncomfortable regardless of the thermostat setting. Smaller structures expose occupants to three, four or even six surfaces with the exterior exposed to the sun and hot outside air. More warm surfaces, more discomfort.
Cooler surfaces, more comfort
If you live in an under-insulated building and don’t mind using more electricity, you can set the thermostat lower. But if the mean radiant temperature is high, a 2 F (1.1 C) drop in air temperature will feel like only 1 F (0.6 C) — and those hot surfaces will still make you feel uncomfortable.
Adding insulation to your roof and replacing single-pane windows with double-pane units with low-emissivity (low-E) glass can help reduce the mean radiant temperature and your energy bills. They’re expensive improvements, but new federal tax credits and forthcoming rebates, to be administered by individual states, can help.
Trees, awnings and exterior shades can also reduce mean radiant temperatures by blocking direct sunlight. However, glass is a lousy insulator, so in very hot climates, single-pane windows completely protected from the sun can still become uncomfortably warm.
Adding a curtain inside — and keeping it closed — can help decrease mean radiant temperature because the curtain will be closer to the air temperature than the glass.
What about renters in old buildings?
Renters in older, under-insulated buildings are often less able to afford large energy bills, and landlords may be unable or unwilling to make expensive improvements. Making matters worse, older air conditioning systems use two to three times as much energy as newer units to deliver the same amount of cooling.
Since creating a comfortable operative temperature requires setting the thermostat lower, an HVAC system in an under-insulated building must work longer and harder, using more energy and further raising the cost. And the costs of discomfort are not only financial: Hot buildings also have adverse impacts on health and productivity.
Millions of Americans now live in places where cooling is the only thing preventing a mass casualty event. In Phoenix, city code requires rental units cooled by air conditioning to maintain a temperature of no more than 82 F (27.8 C), measured 3 feet above the floor in the center of the room. Unfortunately, the code does not specify whether 82 F is the operative temperature or the air temperature.
That one word makes a world of difference.
In an older, under-insulated building similar to my house — or, in what might be the worst-case scenario, a sun-fried southwest unit of the top floor of an uninsulated concrete high-rise — a seemingly safe air temperature of 82 F could easily mask dangerous operative temperatures of 96 F (35.6 C) or higher.
The key to better design
As a professor of architecture and building science, I believe today’s byzantine building codes and rental rules could be greatly improved for comfort by regulating mean radiant temperature rather than air temperature. Vast sections of code could be jettisoned by requiring that interior surfaces, which are easy to measure with an inexpensive infrared thermometer, be kept within a comfort range above 60 F (15.6 C) and below 85 F (29.4 C).
For more comfortable buildings, architects and engineers can apply simple, established principles, such as natural ventilation, shading and the right insulation and windows for the climate. Keeping heat out in the first place means we don’t have to spend so much on energy for cooling. Research shows that these measures can also make us safer by keeping buildings cooler for longer in summer power outages.
The happy result: homes and other buildings that are not only comfortable, but also safer and more affordable to operate.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.


